The basic data types used in Kotlin are strings, characters, booleans, numbers and arrays.
String
- Use double-quotes to define a string.
- Used to store words or sentences.
Character
- Use single-quote to define a character.
- Used to store a single character.
Boolean
- Boolean in Kotlin has only two possible values; true or false.

Numbers
Kotlin provides the following built-in types to represent numbers.
| Data Type | Description | Default Value |
| Byte | 8-bits signed integer | 0 |
| Short | 16-bits signed integer | 0 |
| Int | 32-bits signed integer | 0 |
| Long | 64-bits signed integer | 0L |
| Float | 32-bits floating point number | 0.0F |
| Double | 64-bits floating point number | 0.0 |
As example, define two integers and calculate the total.

The codes above will produce below output.
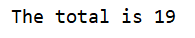
Another alternative to format the output that will also produce the same message as above.

Differences between Double and Float
In Kotlin, a Double variable has a higher-precision since they are 64-bits number (double-precision), whereas a Float is a 32-bits number (single-precision). Depending on your requirements and the data that is going to be stored, choose either one.
To define a float, you need to append the value with a letter “F”, else you will get a compilation error.

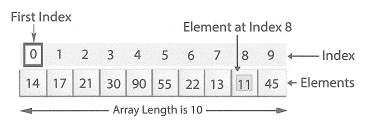
Array
- An array is used to store a list/collection/group of values; all of which have the same data type.
- Its size is fixed i.e. cannot be resized.
- To create an array, use the function arrayOf()
- To access each value (item) in array, use the index.

Image below shows an array of 10 elements. First element’s index is 0, while the last element’s index is 9, respectively.