The statements in your program generally executed from top to bottom.
Control flow statements allows the execution to be broken/interrupted by applying decision making, iteration, branching or conditionally execute a partial part of the program.
This article discuss the decision-making statements (if-then, if-then-else, when), the looping statements (for, while, do-while), and the branching statements (break, continue, return) supported in Kotlin.
Below is a list of conditional operators that can be used in the control flow of the program.
| Operator | Name |
| == | Equal to |
| != | Not Equal to |
| < | Less Than |
| <= | Less Than or Equal to |
| > | Greater Than |
| >= | Greater Than or Equal to |
If Statement
The If statement is a programming conditional statement that, if proved true, executes the true part of the statement. Otherwise, if proved false the program will skip the block and continue with next line of codes.
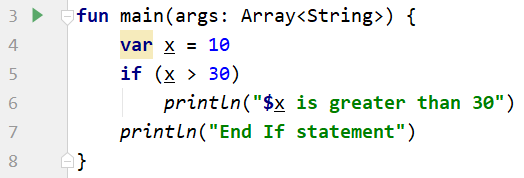
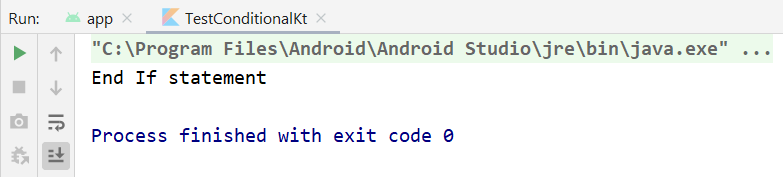
When you run the codes, the output looks like below.
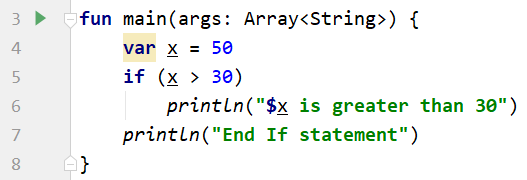
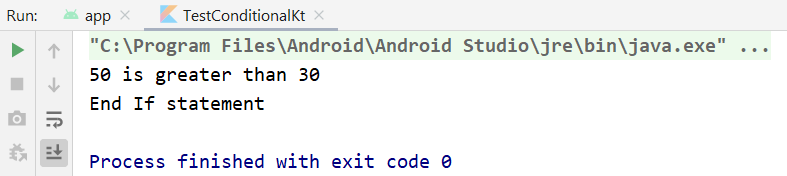
But if you modify the value of x = 50, then a different output will be displayed.
The output.
If-Else Statement
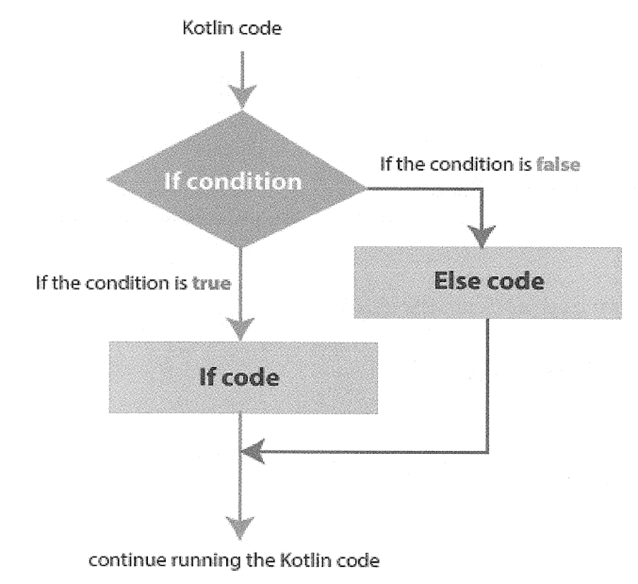
The if-else statement is a bit different. If the condition returns true, it will execute the true block, otherwise it will execute the false (else) block.
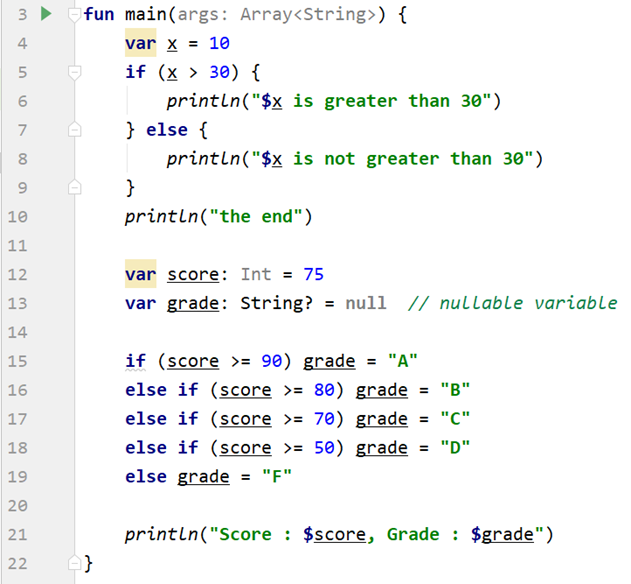
Example below shows if-else and if-else if-else statements.
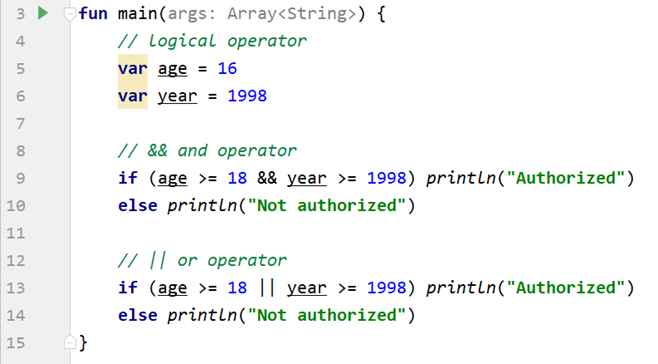
If-Else and Logical Operator
| A | B | A && B | A || B |
| True | True | True | True |
| True | False | False | True |
| False | True | False | True |
| False | False | False | False |
You can use logical operators in an if-statement whenever you have more than one expression to be executed.
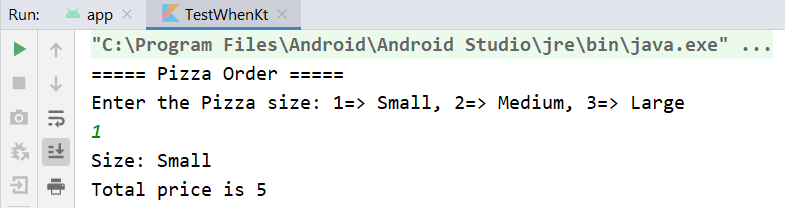
When Statements
When statement is similar to the switch statements in other programming languages such as Java and C++. the when statement can have a number of possible execution paths.

The output of the example codes will look like below.
For Loops
A for loop will iterate a block of statements a certain number of times.

The output of above codes as below.
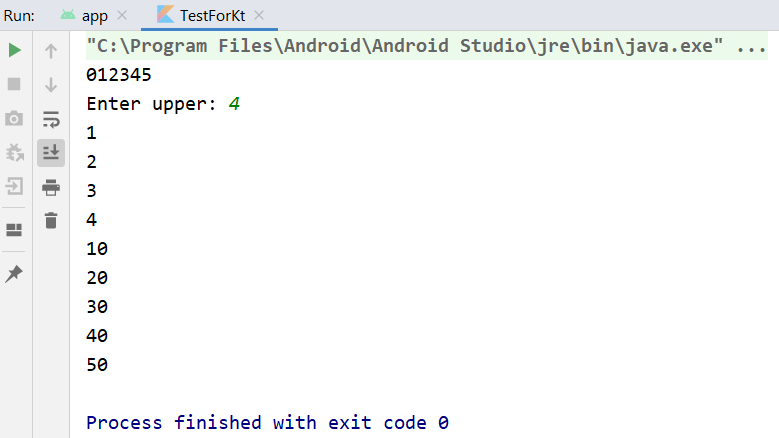
While Loops
While loop will check the condition first; if the condition yields true then it will loop until the condition returns false. A while loop will continue looping as long as the condition returns true.

Below is the output.
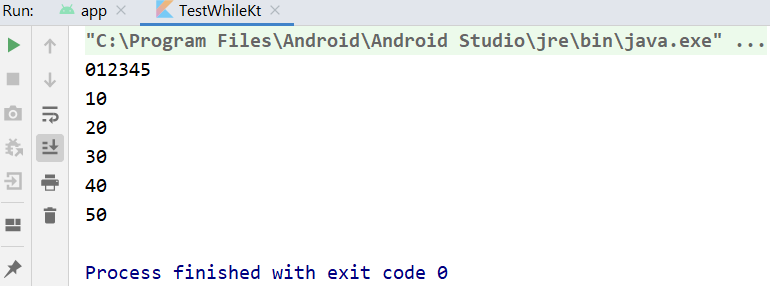
Do-While Loops
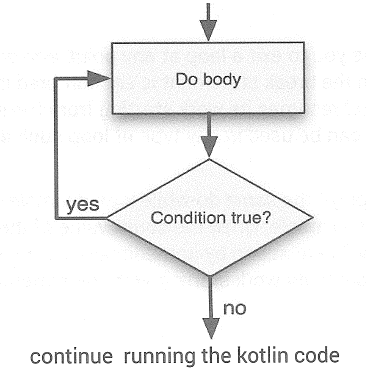
Do-While loop is a bit different from while loop. In do-while loop, it will execute the block first then only check the condition. If the condition returns true, it will continue looping until the condition returns false.
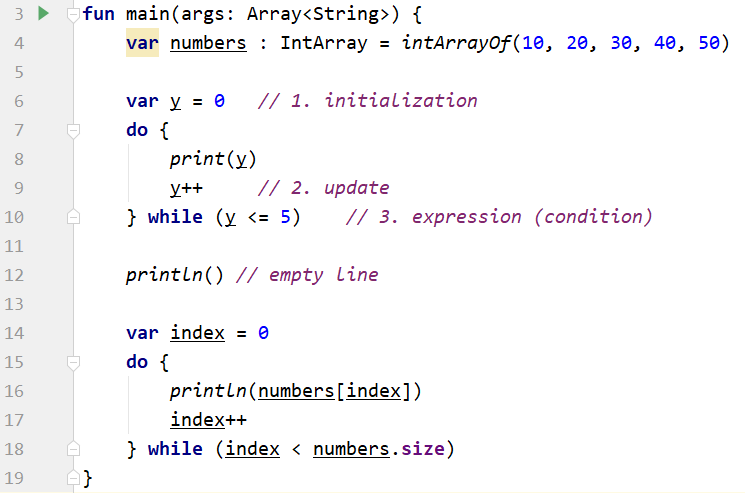
Output of running codes above.
Branching Statements
Kotlin has three branching statements that you can use within your program.
- Break – exit from the current block
- Continue – continue with the next iteration
- Return – return a value and exit from function block

When you run the codes, the output looks like below.

Return branching statement will be discussed in the next post where we’re going to talk about functions.